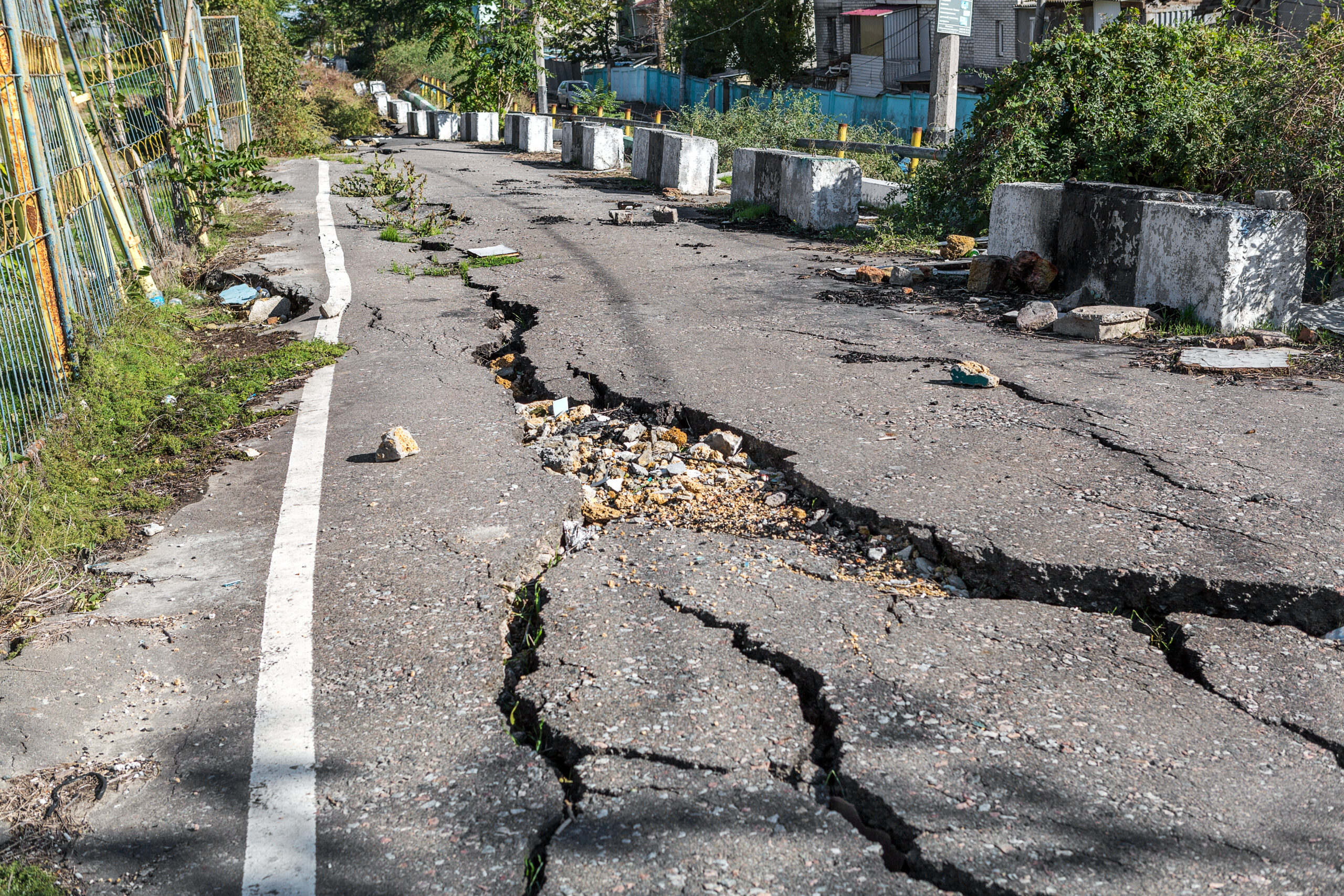
Heavy vehicles such as trucks, buses, and construction equipment place enormous stress on asphalt pavements. Their axle loads are much higher than those of passenger cars, which leads to faster deterioration of asphalt surfaces. Across the United States, this problem worsens under diverse climate conditions and the constant movement of industrial traffic.
Research indicates that pavement damage does not increase linearly with vehicle weight. Instead, the Fourth Power Law demonstrates that the damage grows exponentially with axle load. For instance, a fully loaded 80,000-pound, five-axle truck can cause far more damage to the pavement than a single car. According to a study published by the SciSpace International Journal, this exponential relationship significantly impacts the extent of damage caused by heavier vehicles. This study supersedes the outdated claim that one truck axle equals nearly 10,000 cars.
This article explains how heavy vehicles damage asphalt over time, clears up common myths about truck-to-car damage ratios, and outlines proven strategies to extend pavement life.
Why Heavy Vehicles Cause Disproportionate Damage
The scientific foundation for understanding pavement damage is rooted in the Fourth Power Law, which asserts that pavement damage is exponentially proportional to the axle load. Modern research has replaced earlier estimates that suggested a truck axle causes thousands of times more damage than a car axle. A widely cited study by the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) explains that a typical 80,000-pound, 5-axle truck causes significantly more damage, with research indicating figures in the range of 285 to 343 times more damage than a standard passenger car, aligning with updated standards in the transportation infrastructure field.
This immense stress from freight trucks, construction equipment, and delivery vehicles leads to several common types of damage:
- Cracking: Stress fractures and fatigue (alligator) cracking develop from repeated heavy axle loads.
- Rutting: Grooves form in the wheel paths as the asphalt and its subgrade deform under concentrated, heavy loads.
- Potholes: Water infiltrates the pavement through cracks, weakening the surface and sub-base until it collapses, especially in wet climates.
The Mechanisms of Asphalt Damage
Heavy vehicles damage asphalt through several interconnected mechanisms:
- Load Distribution: Heavy vehicles concentrate immense weight onto a small number of tires, increasing the pounds-per-square-inch pressure on the asphalt surface and the underlying subgrade. This focused load leads to rapid deformation.
- Pavement Fatigue: Just like a paperclip bent back and forth, asphalt loses its flexibility under repeated heavy loads. This structural fatigue leads to the propagation of cracks and eventual surface failure.
- Subgrade Failure: The strength of asphalt is only as good as the foundation beneath it. Weak or improperly compacted subgrades cannot support heavy loads, resulting in depressions, rutting, and potholes. Moisture infiltration is a key factor that accelerates sub-base weakening, often tied to poor drainage issues.
- Overloading: The 2018 study by Shahul Hameed PK and R. Chandra Prathap provides clear evidence that a significant portion of heavy trucks exceed legal weight limits, especially in challenging terrains. Their research quantifies how overloading drastically accelerates pavement damage, particularly on flexible pavements, and leads to increased maintenance costs. The findings highlight the critical need for strict weight enforcement to protect road infrastructure and extend pavement service life.
What Are The Regional and Climate-Based Challenges

The impact of heavy vehicle traffic is amplified by regional climate conditions across the U.S.
- In humid and rainy regions, persistent moisture erodes the sub-base, making pavement more susceptible to rutting and potholes under heavy loads.
- In colder northern states, freeze-thaw cycles cause pavement to expand and contract. This constant movement weakens the asphalt, and when combined with heavy traffic, leads to rapid cracking and deterioration.
Repairs must be tailored to these conditions, prioritizing drainage and water resistance. Areas prone to severe weather, such as hurricanes or heavy snow, require especially resilient and quick repair solutions to minimize downtime, a point often highlighted in NOAA research on infrastructure resilience.
Proactive Solutions to Mitigate Heavy Vehicle Damage
The best defense against heavy vehicle damage is a proactive strategy combining robust design, diligent maintenance, and advanced repair techniques.
- Build Stronger Pavements: Design pavements with increased thickness and stronger aggregate base layers to distribute heavy loads more effectively, as outlined in the FHWA Pavement Design Guide.
- Implement Regular Maintenance: Timely crack sealing, patching, and sealcoating are crucial for preventing water infiltration and subgrade weakening. This approach is a core principle of the FHWA’s pavement preservation guidelines.
- Manage and Enforce Load Limits: Enforcing legal weight limits through weigh stations and other measures is one of the most effective ways to reduce preventable, excessive damage, a strategy supported by the American Trucking Associations (ATA).
- Use Advanced Repair Techniques: When damage occurs, methods like infrared asphalt repair and full-depth reclamation can restore structural integrity far more effectively than simple patching, according to research from the National Asphalt Pavement Association (NAPA).
Why Choose Professional Asphalt Repair Services?
Professional asphalt repair services are expertly equipped to tackle the challenges posed by heavy vehicle traffic:
- Accurate Damage Diagnosis: Experts identify the root cause, whether it’s surface wear or sub-base failure.
- Use of Commercial-Grade Materials and Equipment: Only high-quality materials and advanced tools are used for precise, long-lasting repairs.
- Transparent Estimates and Timelines: Clear, upfront cost breakdowns and realistic project timelines.
- Post-Repair Care Instructions: Ensuring your surface remains durable and in excellent condition after repairs.”
This approach guarantees a lasting solution to keep your asphalt in top condition.
Tips for Maintaining Your Asphalt Pavement
Maintaining your asphalt pavement is crucial for ensuring its longevity and performance. Here are some essential tips to keep your surface in optimal condition.
- Sealcoating: Essential for Long-Lasting Protection
Apply a professional-grade sealcoat every 2–3 years. This creates a strong protective barrier against UV damage, chemicals, and water infiltration, ensuring the longevity of your pavement.
- Regular Inspections: Proactive Care Prevents Major Damage
Conduct routine inspections, particularly after heavy rain, snow, or high traffic. Early detection of cracks or potholes allows for prompt repairs, preventing further deterioration.
- Keep It Clean: Prevent Degradation
Immediately remove oil spills, dirt, and vegetation. These elements can weaken the asphalt binder and potentially obscure underlying issues that require attention.
- Address Repairs Promptly: Minimize Future Costs
Resolve minor cracks and potholes as soon as they appear. Timely repairs prevent small issues from escalating into costly, larger-scale problems that compromise the integrity of your pavement.
Safeguarding Your Asphalt Investment for Long-Term Durability

Heavy vehicles significantly damage asphalt through a combination of concentrated loads, pavement fatigue, and subgrade failure, with these effects worsened by environmental factors like moisture and weather. Understanding these mechanisms and implementing proactive design and maintenance strategies are essential for protecting your investment and extending the life of your pavement.
For expert asphalt repair and maintenance services designed to withstand heavy vehicle traffic and diverse U.S. climates, Contact Asphalt Coatings Company at 337-824-ROCK for a free estimate or consultation.