Creating a durable and reliable asphalt parking lot requires more than pouring pavement. It involves careful planning, site preparation, expert paving techniques, and long-term maintenance strategies. Whether you’re managing a commercial space, an apartment complex, or a high-traffic facility, following a structured process is key to ensuring your parking lot serves its purpose for decades to come.
In this article, we’ll walk through the essential steps to building a strong asphalt parking lot and how partnering with trusted professionals like Asphalt Coatings Company can help you achieve lasting results.
Understanding the Purpose and Scope of Your Parking Lot
Before any design or construction can begin, it’s critical to define the project’s scope and functional goals. This foundational step sets the tone for every phase that follows.
Determining Traffic Load and Use Cases
A parking lot’s design should reflect how it will be used. Will it serve daily shoppers, delivery trucks, or heavy-duty vehicles? High-traffic commercial lots demand thicker asphalt layers and reinforced subbases, while lots serving passenger vehicles may allow for lighter specs. Understanding the load requirements helps avoid premature cracking, rutting, and failure.
Considering Local Regulations and ADA Compliance
In addition to functionality, your parking lot must meet city ordinances, fire codes, and ADA regulations. These include requirements for accessible spaces, ramps, signage, and compliant slopes. By accounting for compliance early, you avoid costly redesigns or legal liabilities down the road.
Importance of Site-Specific Planning in Colorado’s Climate
In regions like Colorado, freeze-thaw cycles pose a serious threat to pavement integrity. A professional contractor like Asphalt Coatings Company considers temperature variations, snow load, and deicing methods when planning materials and drainage to ensure long-term performance.
Conducting a Site Assessment and Soil Evaluation
Building a parking lot without proper site analysis is like building a house without inspecting the foundation—it’s a risk not worth taking.
Geotechnical Testing and Load-Bearing Capacity
A geotechnical evaluation assesses the strength and stability of the soil beneath your parking lot. Engineers test for compaction, moisture content, and bearing capacity to ensure it can support the structure above. Weak or expansive soils may require reinforcement or replacement before proceeding.
Identifying Drainage Patterns and Soil Composition
Water is one of asphalt’s greatest enemies. By analyzing how water moves across and under your site, contractors can plan drainage systems that prevent pooling and erosion. Soil types like clay hold water longer and can cause swelling, so knowing the composition helps inform design decisions.
Site Grading and Elevation Strategy
Proper grading ensures water flows away from the parking surface, reducing the risk of standing water that leads to cracking. Slopes, swales, and catch basins are carefully placed to guide water toward drains or landscaping, keeping the lot dry and structurally sound.
Designing a Durable Asphalt Parking Lot
Once the site is understood, the next step is translating that data into a detailed and functional design.
Choosing the Right Thickness Based on Load Requirements
Thickness matters. For example, a retail parking lot may require 4–6 inches of asphalt, while industrial lots can demand up to 8 inches or more. Skimping on thickness can lead to faster degradation, while overbuilding inflates your budget unnecessarily. Engineers determine the right specs by evaluating use cases and projected lifespan.
Incorporating Drainage Features (Slopes, Drains, Gutters)
Drainage is not just about avoiding puddles—it directly impacts the lot’s durability. Your design should include longitudinal and transverse slopes, trench drains, and perimeter gutters that keep water moving off the surface efficiently. In colder climates, this also prevents freeze-related damage.
Planning for Traffic Flow, Striping, and Accessibility
An effective layout ensures smooth vehicle movement and maximizes space efficiency. Design elements like entry and exit points, traffic islands, speed bumps, and pedestrian crossings should be strategically placed. ADA-compliant features and well-marked spaces enhance usability for all patrons.
Preparing the Subgrade for Long-Term Stability
A strong subgrade is the backbone of any asphalt structure. Preparing it correctly ensures your lot can support heavy traffic without settling or cracking.
Excavation and Removal of Existing Materials
Before new construction begins, old pavement or unsuitable materials must be removed. Failing to excavate properly can trap moisture and cause uneven settling. A clean slate ensures the layers above perform as intended.
Compacting the Subgrade for Load Support
Compaction is critical to eliminate air pockets and ensure uniform support. Contractors use rollers and vibratory equipment to compress the subgrade to industry standards, often achieving 95%+ compaction density for optimal support.
Base Material Selection and Layering
Beneath the asphalt lies a layered foundation—typically made of crushed stone or recycled concrete. These base materials distribute weight evenly and provide a stable platform for the asphalt layers. Asphalt Coatings Company uses proven materials that align with Colorado’s load-bearing and freeze-thaw requirements.
Selecting the Right Asphalt Mix
Not all asphalt is created equal. The right mix provides durability, flexibility, and resistance to environmental stress.
Hot Mix vs. Warm Mix for Commercial Parking Lots
Hot mix asphalt (HMA) is the most common choice, especially for large commercial applications. It offers superior strength and long-term durability. Warm mix asphalt (WMA), on the other hand, is applied at lower temperatures, reducing environmental impact and making it ideal for colder installation windows.
Asphalt Composition and Climate Considerations
Asphalt must be engineered to handle specific regional climates. In Colorado, where temperatures can swing dramatically, asphalt mixes are often modified with polymers to increase flexibility and reduce cracking.
Importance of Professional Recommendations from Experts like ACC
Experienced contractors like Asphalt Coatings Company assess project needs and recommend the best mix based on performance, cost-efficiency, and environmental factors. Their in-house expertise ensures your mix will stand up to time and traffic.
Comparison Table: Hot Mix Asphalt vs. Warm Mix Asphalt
| Feature | Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) | Warm Mix Asphalt (WMA) |
| Application Temperature | 275°F – 325°F | 200°F – 275°F |
| Durability | High | Moderate to High |
| Environmental Impact | Higher Emissions | Lower Emissions |
| Cold Weather Suitability | Less Suitable | More Suitable |
| Compaction Time | Faster Cooling | Slower Cooling (More Work Time) |
| Cost | Typically Lower | Slightly Higher |
Proper Asphalt Paving Execution
This is where the groundwork turns into reality. The paving stage must be executed with precision, timing, and quality control.
Layer-by-Layer Asphalt Installation Process
Paving involves laying down multiple layers of asphalt, typically in lifts of 2–3 inches. Each layer is compacted before the next is added. This method increases structural integrity and helps the pavement withstand daily stress.
Compaction for Smoothness and Density
Each lift must be compacted with high-pressure rollers to remove air voids, ensure tight bonds between layers, and achieve the desired density. Proper compaction enhances load distribution and prevents early surface wear.
Paving in Optimal Weather Conditions
Asphalt must be laid during dry, moderate weather. Ideal temperatures range between 50°F and 85°F. Paving outside these conditions can affect adhesion and curing, shortening the pavement’s lifespan.
Striping and ADA-Compliant Markings
Once the asphalt cools, clear striping and signage turn the surface into a usable parking lot.
Line Marking Techniques for Visibility and Durability
Using traffic-grade thermoplastic or epoxy paint, contractors mark lanes, spaces, and directional arrows. Reflective paints are often used to improve nighttime visibility and enhance driver safety.
ADA Ramps and Signage Requirements
Compliance with ADA standards includes marked accessible spaces, appropriate signage, and properly graded curb ramps. These features not only meet legal standards but show your commitment to inclusivity.
Enhancing Safety Through Clear Directional Striping
Well-planned markings reduce traffic confusion and pedestrian hazards. Features like arrows, stop bars, and crosswalks direct traffic effectively and minimize risk.
Final Surface Treatments and Seal Coating
Protecting your investment means applying the right surface treatments at the right time.
Benefits of Seal Coating for Protection and Longevity
Seal coating forms a protective barrier over your asphalt, shielding it from UV rays, water, oil, and chemicals. It also restores the deep black color of the pavement, improving curb appeal.
Anti-Skid Surfaces and UV Resistance
Certain sealants include aggregate or additives that enhance skid resistance and improve safety, especially in wet or snowy conditions. UV-resistant coatings further prevent surface degradation.
Timing Your First Seal Coat
The first seal coat is typically applied 6–12 months after installation. After that, reapplications every 2–3 years can extend the life of your lot significantly.
Creating a Maintenance Plan for Longevity
No asphalt surface is truly maintenance-free, but a proper maintenance plan can minimize disruptions and major repairs.
Scheduled Inspections and Crack Sealing
Annual or biannual inspections help detect early signs of cracking or heaving. Crack sealing promptly prevents water from penetrating the subbase and causing further damage.
Routine Seal Coating and Restriping
Seal coating and restriping on a regular schedule maintain both the appearance and functionality of the parking lot. It also keeps your lot in compliance with changing codes and safety requirements.
Partnering with Experts for Long-Term Success
Asphalt Coatings Company offers tailored maintenance programs that include everything from pothole repairs to trip hazard remediation, helping you preserve your lot without unexpected expenses.
Budgeting and ROI Considerations
Understanding your return on investment can help you make smarter decisions.
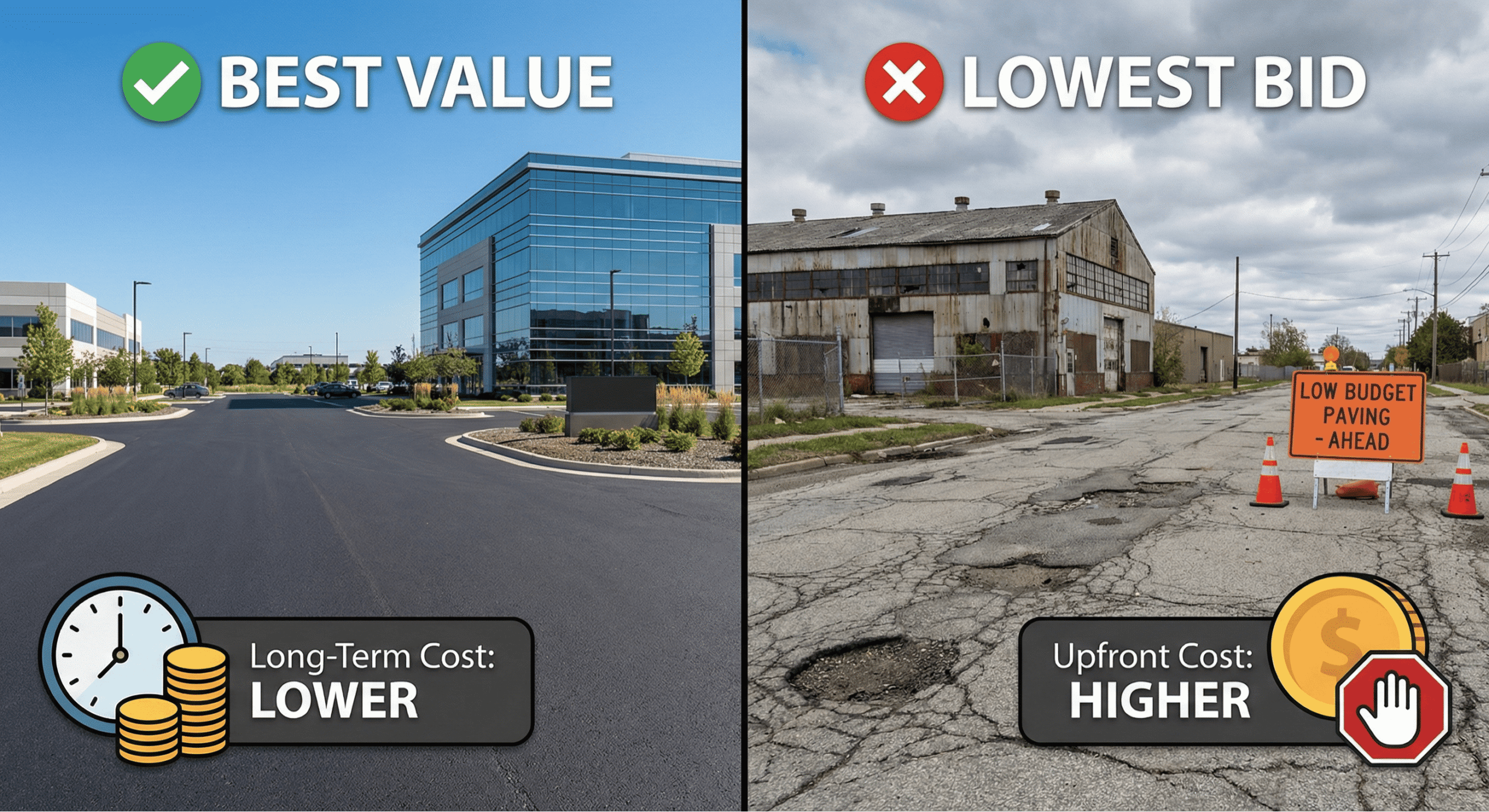
Understanding Short-Term vs. Long-Term Costs
Cutting corners on materials or preparation may save money upfront but will lead to higher repair and replacement costs over time. Investing wisely from the beginning pays off.
Value of Durability and Low-Maintenance Design
A well-built asphalt parking lot can last 20–30 years with proper maintenance. Lower maintenance needs and fewer repairs mean more savings over the lot’s lifetime.
ROI on High-Quality Asphalt Parking Lots
A strong, visually appealing parking lot boosts property value, attracts tenants, and reduces liabilities—an ROI that continues to pay dividends.
Why Choose Asphalt Coatings Company for Your Parking Lot Project
Asphalt Coatings Company brings over 35 years of experience in designing, building, and maintaining commercial parking lots across Colorado. With a commitment to craftsmanship, compliance, and customer service, their full-service solutions ensure your project is done right—on time, on budget, and built to last.
Ready to start your next parking lot project? Contact Asphalt Coatings Company today for a free quote and professional consultation.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How often should an asphalt parking lot be inspected?
A commercial asphalt lot should be inspected at least once a year to identify surface issues, cracks, and drainage concerns.
2. What are signs that my asphalt parking lot needs repair or replacement?
Visible potholes, large cracks, standing water, and faded markings are all signs that repair or even reconstruction may be needed.
3. Can asphalt be recycled during repaving?
Yes, reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) is often reused in new paving projects, making it a sustainable and cost-effective option.
4. What’s the typical lifespan of an asphalt parking lot?
With proper design, installation, and maintenance, a commercial asphalt parking lot can last 20–30 years or more.
5. How do I prepare for a paving project on an active commercial site?
Work with an experienced contractor who can phase construction, work off-hours, and minimise disruption to tenants or customers.